What’s this WiFi all about?
WiFi, we all use it, some of us love it, some of us hate it (usually only when it’s not working); but if you’ve ever setup a new router or peeked at those advanced settings on the wireless router, you might have thought that those menus were populated by kids just learning their ABC’s; 2.4GHz, 5GHz, a/b/g/n/ac, who talks like that?!
Let’s see if we can’t break this down without getting too ‘techy’.
In the world of wifi there are two primary things to be aware of:
1. The frequency at which your devices operate (2.4GHz or 5GHz)
2. The wireless protocol your devices support (802.11 a/b/g/n/ac)
Depending on the mix of devices that you own, and the age of them, you may find that you have a mix of both frequencies and various wireless protocols to support on your network and you will often find that a “dual band” router is best suited for your needs. These dual band units broadcast both frequencies simultaneously, often times allowing your device to ‘decide’ which frequency/band to use.
The break down – 2.4GHz vs. 5GHz
The 2.4GHz spectrum is the most common space and as a result has the largest number of devices supported for it. Everything from microwaves and Bluetooth to TV and radio operate on this frequency, and with only 3 non-overlapping channels (1, 6 & 11) there’s also the largest amount of interference in this space, as you can imagine.
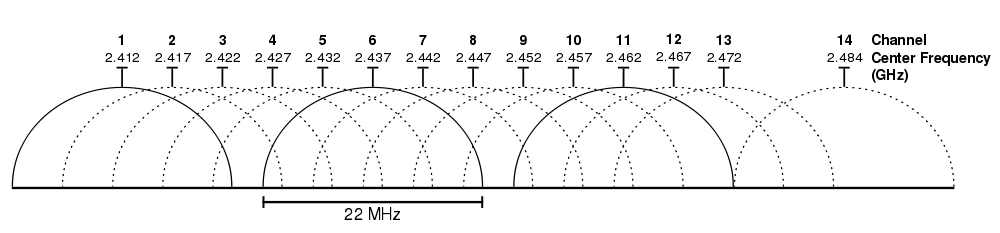 image source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:2.4_GHz_Wi-Fi_channels_(802.11b,g_WLAN).svg
image source: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:2.4_GHz_Wi-Fi_channels_(802.11b,g_WLAN).svg
The 5GHz spectrum is a much larger highway then the 2.4GHz space as it offers as many as 21 non-overlapping channels (in the U.S.) and as a result is not susceptible to the interference found on the 2.4GHz spectrum.
As for the wireless protocols, 802.11a/b/g/n/ac, each of these letters represents which IEEE 802.11 revisions are supported on the router with 802.11n and 802.11ac being the newest standards and all other standards considered ‘legacy’ devices.
|
Band/Frequency |
Channels |
802.11 Standards |
Network Range |
Interference |
Bandwidth |
|
2.4 GHz |
3 non-overlapping |
b/g/n |
Wider Range |
Higher |
Lower |
|
5 GHz |
21 non-overlapping |
a/n/ac |
Shorter Range |
Lower |
Higher |

